
The calculation assesses how the growth in sales and profits are linked to each other in a business. Based on the contribution margin formula, there are two ways for a company to increase its contribution margins; They can find ways to increase revenues, or they can reduce their variable costs. A key characteristic of the contribution margin is that it remains fixed on a per unit basis irrespective of the number of units manufactured or sold. On the other hand, the net profit per unit may increase/decrease non-linearly with the number of units sold as it includes the fixed costs. In the above example we calculated contribution per unit by subtracting variable cost per unit from selling price per unit. In accounting, contribution margin is the difference between the revenue and the variable costs of a product.
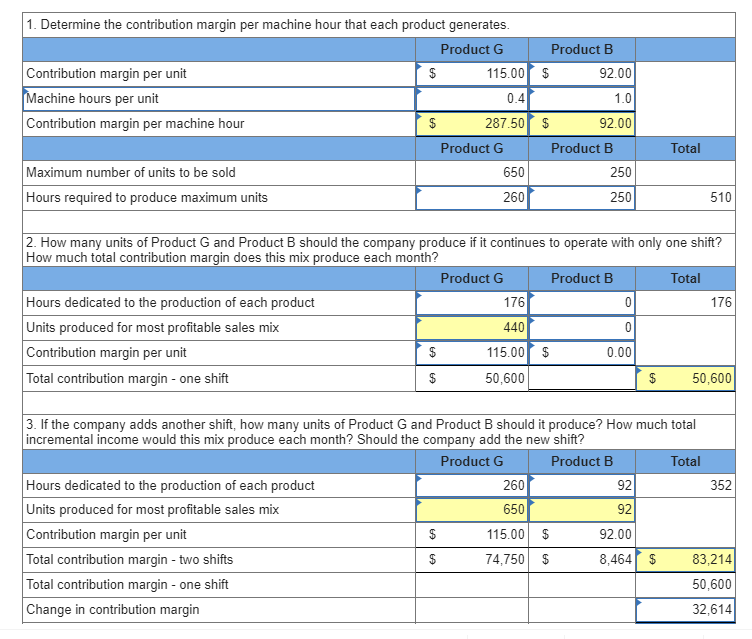
How do you find the contribution margin per direct labor hour?
Because it is calculated by subtracting variable costs from sales revenue, it surfaces the incremental profit earned for each unit sold and indicates how much revenue contributes to your fixed costs and profits. By analyzing the unit contribution margin of different products or units, companies can identify their most profitable offerings and allocate resources accordingly. Additionally, it assists in setting pricing strategies to ensure that products are priced appropriately to cover both variable and fixed costs while maximizing overall profitability. Overall, the unit contribution margin provides valuable insights into the financial performance of individual products or units and helps guide strategic decision-making within organizations.
Is a high contribution margin ratio good?
A contribution margin ratio of 40% means that 40% of the revenue earned by Company X is available for the recovery of fixed costs and to contribute to profit. On the other hand, variable costs are costs that depend on the amount of goods and services a business produces. The more it produces in a given month, the more raw materials it requires.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
Some income statements report net sales as the only sales figure, while others actually report total sales and make deductions for returns and allowances. Either way, this number will be reported at the top of the income statement. But remember, some products will not reach profitability until reaching the ideal volume of units sold. If you find yourself in this situation, ask yourself if it is worth going the extra mile on input to reach desired results. The contribution margin (CM) is the amount of revenue in excess of variable costs. Streamlining your operations to reduce waste and improve productivity will help to reduce your variable costs.
- Fixed costs and variable costs vary for every company as each has its unique business model, product line, operational structure, and production inputs.
- In other words, it measures how much money each additional sale “contributes” to the company’s total profits.
- The key component of the contribution per unit calculation that can cause difficulty is the variable cost.
- However, the growing trend in many segments of the economy is to convert labor-intensive enterprises (primarily variable costs) to operations heavily dependent on equipment or technology (primarily fixed costs).
This metric is typically used to calculate the break even point of a production process and set the pricing of a product. They also use this to forecast the profits of the budgeted how to find contribution per unit production numbers after the prices have been set. Contribution margin analysis is a measure of operating leverage; it measures how growth in sales translates to growth in profits.
Contribution Margin Per Unit Formula:
A unit contribution margin is a straightforward way to assess if your product can cover production expenses. Instead of doing contribution margin analyses on whole product lines, it is also helpful to find out just how much every unit sold is bringing into the business. The profitability of our company likely benefited from the increased contribution margin per product, as the contribution margin per dollar increased from $0.60 to $0.68. The analysis of the contribution margin facilitates a more in-depth, granular understanding of a company’s unit economics (and cost structure). The contribution margin ratio is calculated as (Revenue – Variable Costs) / Revenue. A low margin typically means that the company, product line, or department isn’t that profitable.
As we said earlier, variable costs have a direct relationship with production levels. When only one product is being sold, the concept can also be used to estimate the number of units that must be sold so that a business as a whole can break even. For example, if a business has $10,000 of fixed costs and each unit sold generates a contribution margin of $5, the company must sell 2,000 units in order to break even. However, if there are many products with a variety of different contribution margins, this analysis can be quite difficult to perform. While products with a high contribution margin per unit are the gems of your business, in this case, the more units sold for a good with a high unit contribution margin, the easier it is to cover fixed costs.
Using the provided data above, we can calculate the price per unit by dividing the total product revenue by the number of products sold. On the other hand, the gross margin metric is a profitability measure that is inclusive of all products and services offered by the company. However, the contribution margin facilitates product-level margin analysis on a per-unit basis, contrary to analyzing profitability on a consolidated basis in which all products are grouped together. Therefore, the contribution margin reflects how much revenue exceeds the coinciding variable costs. With a high contribution margin ratio, a firm makes greater profits when sales increase and more losses when sales decrease compared to a firm with a low ratio. Alternatively, the company can also try finding ways to improve revenues.
